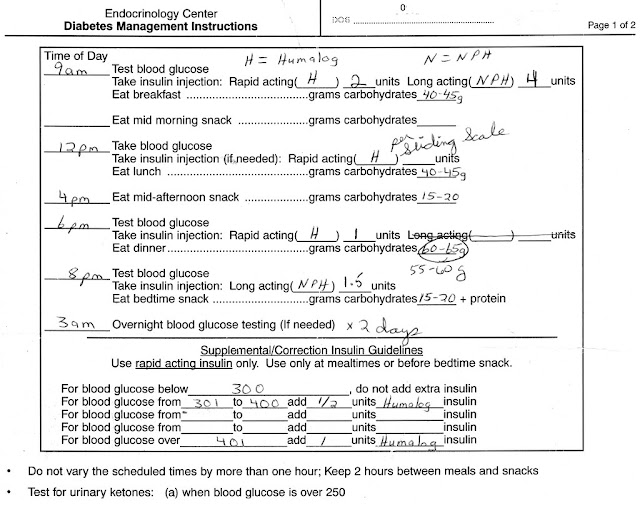
Diabetes is a complex and chronic medical condition that affects the way our bodies process glucose, a type of sugar that provides us with energy. Diabetes is primarily categorized into two main types: type 1 and type 2.In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that Produce insulin, an essential hormone for the regulation of blood sugar levels. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes have little to no insulin in their bodies and require daily insulin injections to survive.
Conversely, type 2 diabetes develops when the body either becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce sufficient insulin to regulate blood sugar levels adequately.
While lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a significant role in the development of type 2 diabetes, genetics and other factors also contribute. Initially, type 2 diabetes can often be managed with oral medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes, injected medications. However, as the disease progresses, some individuals may require insulin injections to control their blood sugar levels effectively.
Understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach, including the use of insulin injections. In the following sections, we will explore how insulin works in the body, the various types of diabetes, insulin treatment options, and why some diabetes patients may require insulin injections as part of their treatment plan.
How Insulin Works in the body
Insulin, a hormone essential for blood sugar level regulation, is produced by the pancreas.When we eat, our bodies break down the carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, which allows the glucose to enter our cells, where it is used for energy. This process helps to keep our blood sugar levels in a healthy range.
For individuals with diabetes, however, this process doesn't work as it should. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, leaving the body with little to no insulin. As a result, blood sugar levels can rise to dangerous levels. Type 2 diabetes arises when the body develops resistance to insulin or produces an insufficient quantity of it, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
Insulin injections are a common treatment for diabetes because they provide the body with the insulin it needs. By injecting insulin into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin, it is absorbed into the bloodstream and can effectively regulate blood sugar levels. Various types of insulin exist, each characterized by its specific onset and duration of action. Some types act quickly and are used to control blood sugar spikes after meals, while others provide a slow and steady release of insulin throughout the day.
It's important to note that insulin injections are not a cure for diabetes but rather a way to manage the condition. They need to be taken consistently and in the correct dosage to ensure that blood sugar levels remain stable. With proper management and the support of healthcare professionals, insulin injections can help individuals with diabetes live healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Types of Diabetes and Insulin Treatment Option
Type 1 diabetes involves an autoimmune response where the immune system targets and eliminates the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes have little to no insulin in their bodies and require insulin injections for survival.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels. Initially, type 2 diabetes can often be managed with oral medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes, injected medications. However, as the disease progresses, some individuals may require insulin injections to control their blood sugar effectively.
Insulin treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of diabetes. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are the primary method of treatment. They can choose between rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, depending on their needs.
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin treatment may be introduced when other medications and lifestyle changes are no longer sufficient to control blood sugar levels. In these cases, a doctor may prescribe insulin injections to help regulate glucose levels.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable insulin treatment options based on individual circumstances and needs. They can provide guidance on dosage, timing, and any potential side effects of insulin therapy.
In the next section, we will explore why some diabetes patients require insulin injections as part of their treatment plan

Why Some Diabetes Patients Require Insulin Injections
Insulin injections are an essential part of treatment for many patients with diabetes, but why exactly do some individuals require them? The need for insulin injections depends on several factors, including the type and severity of diabetes, as well as individual circumstances.
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin injections are necessary because their immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. As a result, they have little to no insulin in their bodies, and daily injections are crucial for their survival. Without these injections, their blood sugar levels can become dangerously high.
In type 2 diabetes, insulin injections may be required when other medications and lifestyle changes are no longer effective in controlling blood sugar levels. This usually happens as the disease progresses, and the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough of it.
Additionally, some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin injections during periods of illness or stress, when blood sugar levels are harder to control.
It's important to note that the decision to start insulin injections is made by healthcare professionals based on individual needs. Regular monitoring and communication with healthcare providers are essential for adjusting insulin dosage and ensuring the most effective treatment plan
Benefits and Risks of Insulin Injections
Insulin injections are a vital aspect of diabetes management for many patients, offering a range of advantages that can significantly enhance an individual's quality of life. The primary advantage of insulin injections lies in their capacity to effectively regulate blood sugar levels. By supplying the body with the necessary insulin, injections help maintain glucose levels in a stable range, preventing dangerous fluctuations.
In addition to their role in controlling blood sugar, insulin injections can also aid in the management of complications associated with diabetes. They can lower the risk of heart disease, nerve damage, kidney issues, and eye problems, all of which are frequent consequences of poorly controlled diabetes.
While insulin injections bring numerous benefits, it is important to remain cognizant of potential risks and challenges associated with this form of treatment. One of the primary risks is the potential for hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, which can occur if the insulin dose is excessive or if meals are skipped. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include tremors, perspiration, dizziness, and confusion. It is imperative to regularly monitor blood sugar levels and make necessary adjustments to the insulin dosage to prevent this occurrence.
Other potential risks encompass reactions at the injection site, weight gain, and allergic responses. Nevertheless, with proper technique, vigilant monitoring, and transparent communication with healthcare providers, these risks can often be effectively managed
 |
This Helps in Diabetes
|
Tips for Managing Insulin Injections Effectively
Managing insulin injections effectively is essential for individuals with diabetes to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Here are some pointers to assist you in navigating the process.
1. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions: Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and timing for your insulin injections. It is crucial to follow their instructions carefully and not make any changes without consulting them.
2. Inject insulin in the correct locations: Rotate injection sites to prevent the development of lumps or skin reactions.
Typical injection locations encompass the abdominal area, thighs, and upper arms.. Consult with your healthcare provider to ensure you are injecting in the correct areas.
3. Use the right technique: Clean the injection site with alcohol before injecting and make sure to properly dispose of used needles in a sharps container. Practice proper injection technique to minimize discomfort and the risk of infection.
4. Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Regularly checking your blood sugar levels helps you adjust your insulin dosage as needed. Work with your healthcare provider to determine the frequency and timing of these checks.
5. Communicate with your healthcare provider: Stay in touch with your healthcare provider to discuss any concerns, side effects, or changes in your condition. They can offer assistance and encouragement to aid you in effectively managing your diabetes
By following these tips and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you can ensure that your insulin injections are administered correctly and effectively manage your diabetes. Remember, managing diabetes is a journey, and with the right strategies, you can lead a healthy and fulfilling life.